Understanding the Technical Jargon of Graphics Processing Unit Specifications
GPUs, commonly known as GPUs, are now a critical part in modern computing, especially in gaming, graphic design, and artificial intelligence. As technology continues to evolve, understanding GPU specifications is crucial for anyone looking to buy a new graphics card and upgrade their existing one. The diverse range of terms along with measurements can be overwhelming, yet a clear comprehension of these specs can empower you to make wise choices.
From memory bandwidth and CUDA cores, every specification is crucial in the performance of a GPU. These technical terms often sound daunting, yet knowing their meanings and how they affect performance is key for maximizing your hardware's potential. In this article will break down various GPU specifications you frequently encounter, helping demystify the jargon and making it easier for you to choose a suitable graphics card for your needs.
Key Graphics Processing Unit Specs Detailed
In examining GPU specifications, one of the most important aspects to consider is the core count. The core count indicates how many processing units are available to process tasks at the same time. This number directly influences the efficiency of the GPU, especially in tasks that require parallel processing, such as rendering graphics and performing simulations. In general, a increased core count indicates enhanced capability in gaming and professional use, leading to better frame rates and improved rendering times.
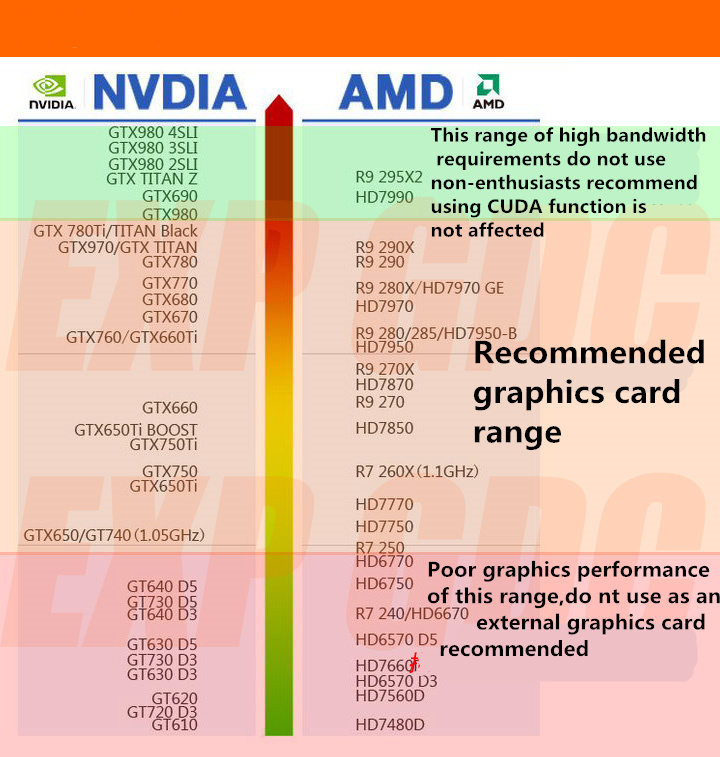
Another critical specification is the memory bandwidth, which shows the amount of data a GPU can read from or send to its memory in a specific time frame. It is influenced by both the memory type and the width of the memory bus. Increased memory bandwidth means faster data transfer speeds, which are essential for demanding applications like gaming at 4K resolution and AI workloads. Grasping how memory bandwidth interacts with core count can help users evaluate the overall capabilities of a GPU for specific applications.
The clock speed is a further vital metric, showing how fast the GPU can execute instructions. Quantified as megahertz or gigahertz, a greater clock frequency generally results in superior capability, as it allows the GPU to handle a greater number of instructions per second. Still, clock speed must not be considered alone; it should be evaluated with the number of cores and bandwidth to get a full understanding of a GPU’s capabilities. Balancing these metrics is crucial for picking the right GPU for different uses, whether for gaming experiences, media production, or scientific computations.
Performance Metrics to Take into Account
When assessing GPU specifications, performance indicators play a vital role in establishing the fitness of a graphics card for certain applications. Clock speed, usually measured in MHz, indicates how quickly a GPU can process data. Elevated gpuprices.ai translate to superior performance, notably in gaming and demanding applications. However, clock speed alone does not provide a complete picture; it must be factored in alongside additional metrics such as core count and architecture.
Another important metric is the number of CUDA cores, or stream processors, which indicate the ability to process in parallel of the GPU. A greater core count typically increases the efficiency of a GPU when handling complex calculations and rendering graphics. This is notably important in cases like 3D rendering, video editing, and machine learning. It's also worth noting that the performance of the GPU architecture influences how well the cores can perform, making architecture a key element to evaluate alongside core count.
The memory bandwidth and VRAM size also considerably influence a GPU's performance. Memory bandwidth is the capacity at which data can be retrieved from or written to the memory by the GPU, while VRAM size determines how much data can be stored and retrieved at once. For tasks such as gaming at high resolutions or working with big data in graphics applications, ample VRAM is paramount to ensure smooth performance. Therefore, when evaluating GPU specs, one must consider these metrics in conjunction to ensure optimal performance for your specific needs.
Picking the Appropriate GPU for Your Needs
Selecting the right GPU depends on grasping your exact requirements and capability requirements. If you're a gamer, search for a graphics card that handles the most recent titles and offers high frame rates at your chosen resolution. Elements such as VRAM, clock speeds, and compatibility with technologies like ray tracing can greatly enhance your gaming experience. For informal gaming, mid-range options might suffice, while competitive gamers usually need premium models to maintain peak performance.
For content creators, a GPU's abilities in handling tasks like video editing, 3D rendering, and graphic design are crucial. GPUs designed for high-end workloads often come with extra features such as enhanced memory bandwidth and ability to handle multiple displays. It's important to balance power with financial considerations, as higher specs can lead to greater costs. Evaluating benchmarks for software compatibility can provide clarity into which cards meet your design needs.
Finally, if you're curious in machine learning or AI development, performance metrics such as CUDA cores and tensor cores become important. These attributes indicate how well a GPU can process parallel processing workloads, which are common in training models. Investigating current trends in GPU technology can aid you decide on an informed decision that aligns with your tech pursuits and upgrading your setup.